Anti-TIGIT (Hu) aus Maus (TG1) – unkonj.
-
Übersicht
Artikelnummer DIA-TG1-M Spezifität TIGIT (T-cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains, VSTM3)
Spezies-Reaktivität Immunogen Rekombinantes Peptid der extrazellulären Domäne von humanem TIGIT
Wirtsspezies Isotyp Klon Klonalität (Mono-/Polyklonal) Anwendung Konjugation Verdünnung Format 0,05% NaN3, 2% BSA, gereinigter Antikörper (aus Kulturüberstand), in PBS (pH 7,4), Lyophilisat
Produktlinie / Thema Zweckbestimmung Temperatur - Lagerung Temperatur - Transport Suchcode Hersteller / Marke Uniprot_ID Gene_ID Alias T-cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains, TIGIT, V-set and immunoglobulin domain-containing protein 9, V-set and transmembrane domain-containing protein 3
- Datenblätter und Downloads
-
Weitere Produktinformationen
Reactivity
Clone TG1 is the first monoclonal antibody detecting TIGIT (T cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains) in routine formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue specimen. It has been validated for the identification of TIGIT positive T-cells infiltrating human tumors in order to allow the detection of TIGIT in the tumor microenvironment under pathological conditions.
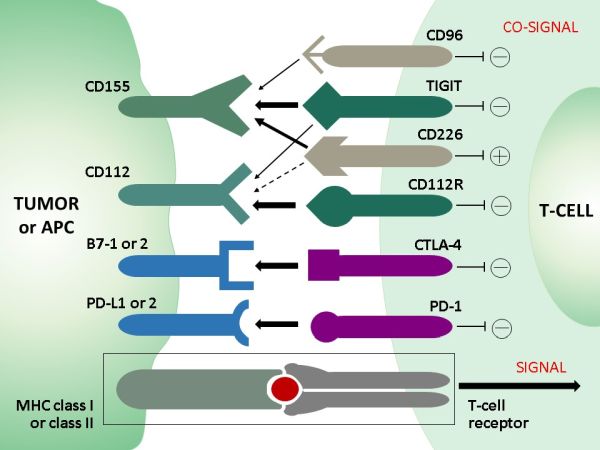
TIGIT (T-cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains) is a member of the poliovirus receptor (PVR) family and acts as an im-mune checkpoint protein expressed on subsets of T lymphocytes. The expression of TIGIT has been reported on NK cells, regu-latory T cells, follicular T helper cells, memory CD4+ T cells, and CD8+ T cells, but it is not expressed on B cells or naive CD4+ T cells. TIGIT may be upregulated on naive CD4+ T cells upon activation. TIGIT has been shown to be upregulated on T cells in multiple cancer models. The ligands CD155 and CD112 are also highly expressed on dendritic cells and macrophages in several types of cancer. Additionally, TIGIT expression is highly correlated with the expression of other coinhibitory molecules, including PD-1. In addition to directly inhibiting cytotoxic T-cell activity, TIGIT can foster an immunosuppressive microenvironment through its impact on other immune cells, for example, by binding to CD155 on the surface of dendritic cells or by manipulating NK cell activity. TIGIT inhibiting drugs are currently being developed. Immunohistochemical application of monoclonal antibody TG1 may provide valuable information for clinical research and potential therapeutic interventions specifically targeting the TIGIT-related tumor immunology checkpoint.Immunohistochemistry of human TG1 in routine formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue samples
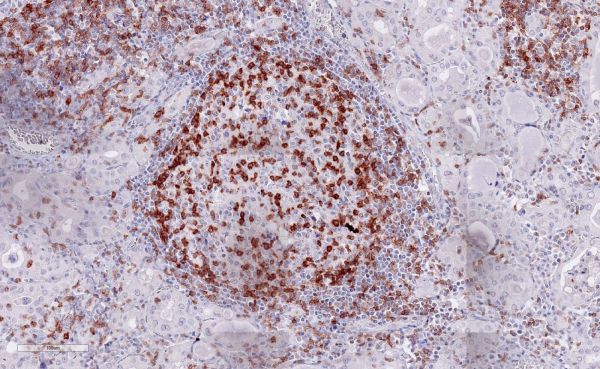
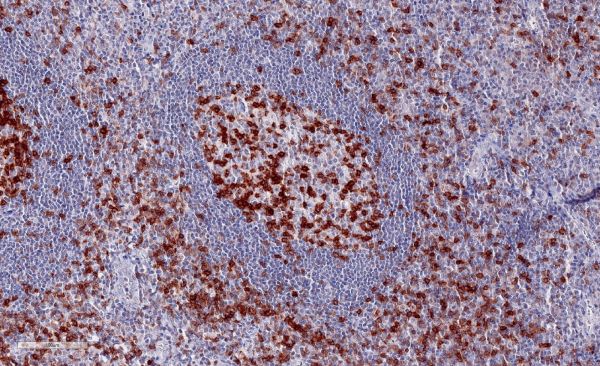
A: Normal human tonsil with numerous TIGIT-positive lymphocytes
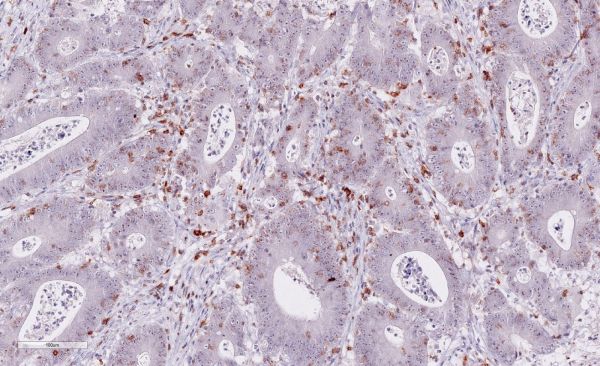
B: Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in colorectal carcinoma
C: Inflamatory lymphoid infiltrate in Hashimoto thyroiditis
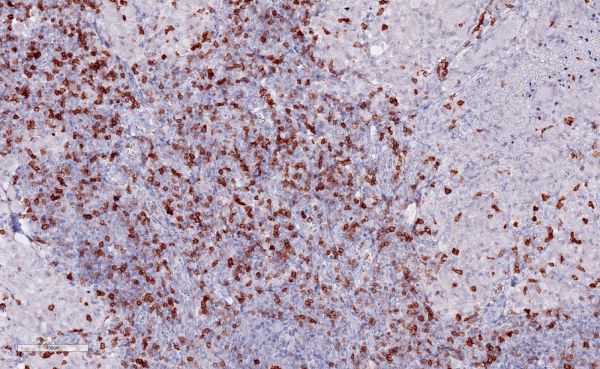
D: Sarcoid granuloma interspersed with TIGIT-positive lymphocytes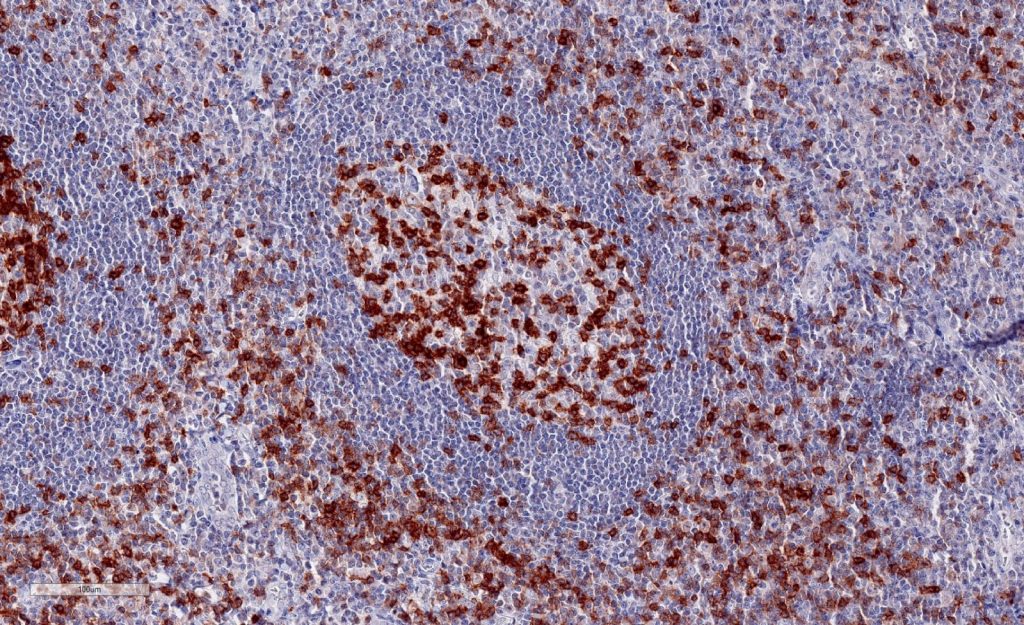
(A) Tonsil

B) Colorectal carcinoma
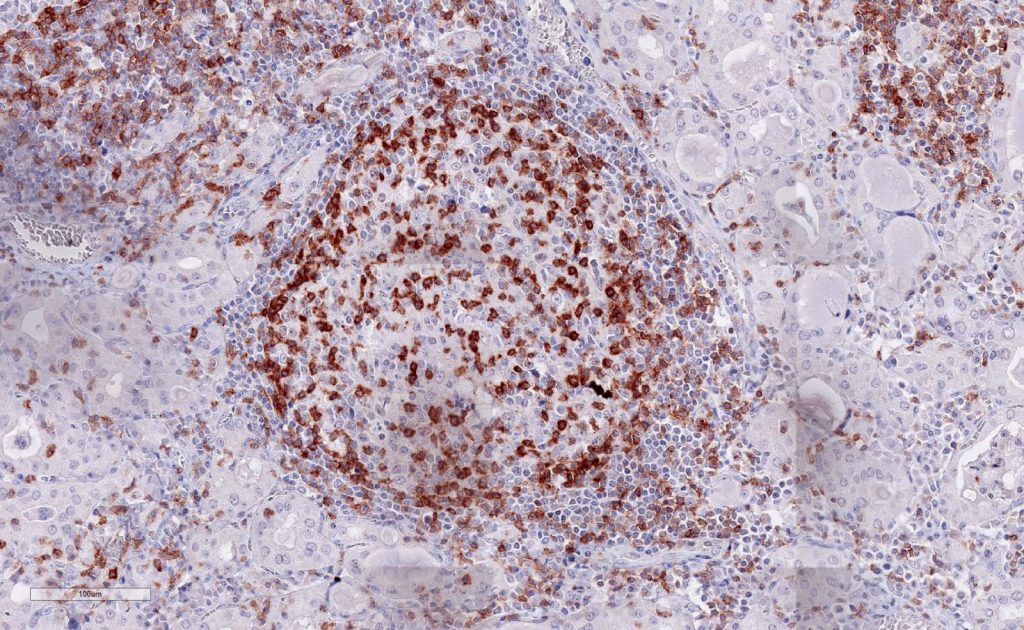
(C) Hashimoto thyreoiditis
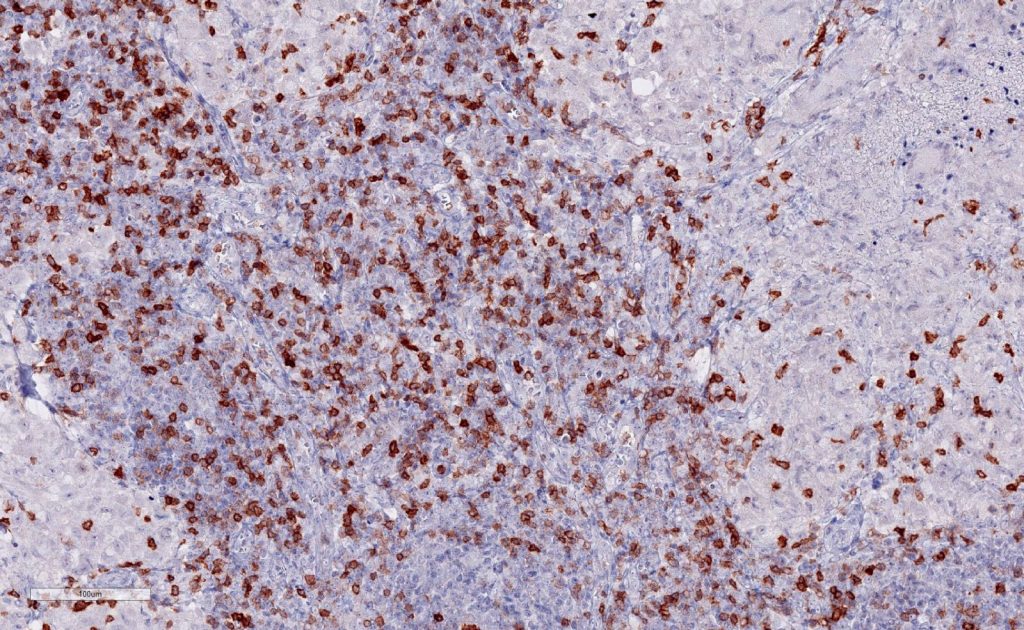
(D) Sarcoid granuloma
(pictures courtesy of Prof. Guido Sauter, Department of Pathology, University Hospital Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany)
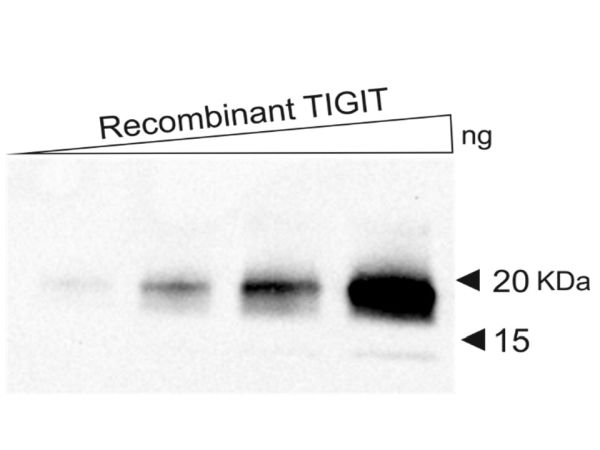
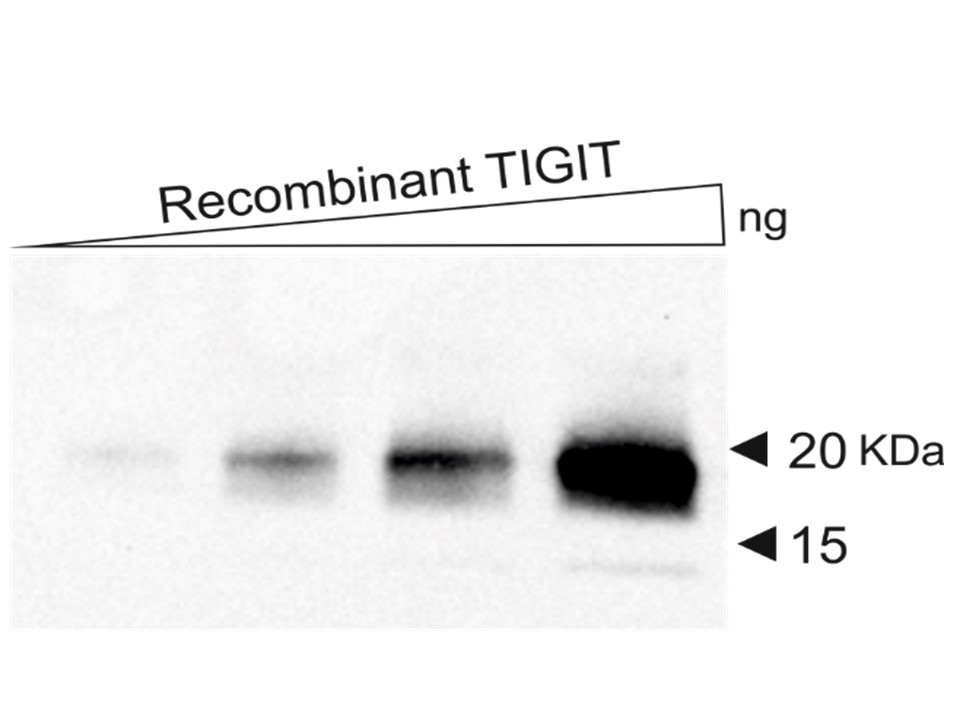
Western blot performed with DIA-TG1 (1:500) on recombinant human TIGIT
References for Clone TG1
- Niebel D et al. DNA methylation regulates TIGIT expression within the melanoma microenvironment, is prognostic for overall survival, and predicts progression‑free survival in patients treated with anti‑PD‑1 immunotherapy. Clinical Epigenetics 14:50 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13148-022-01270-2 (2022)
- Annibali, O., Bianchi, A., Grifoni, A. et al. A novel scoring system for TIGIT expression in classic Hodgkin lymphoma. Sci Rep 11, 7059. https://doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86655-8 (2021)
- Scimeca, M. et al. Programmed death ligand 1 expression in prostate cancer cells is associated with deep changes of the tumor inflammatory infiltrate composition. Urol. Oncol. 37, 297.e19-297.e31. https://doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2019.02.013 (2019).
- Hinsch A et al. Expression of the immune checkpoint receptor TIGIT in seminoma. Oncol Lett. 2019 Aug;18(2):1497-1502. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6607271/
- Blessin NC et al. Patterns of TIGIT expression in normal lymphatic tissue, inflammation and cancer. Disease Markers, Volume 2019, Article ID 5160565, 13 pages, https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/5160565
- Li W et al. Expression of the immune checkpoint receptor TIGIT in Hodgkin’s lymphoma. BMC Cancer 2018, 18:1209, https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-5111-1
General References
- Blake SJ et al. Molecular pathways: targeting CD96 and TIGIT for cancer immunotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2016; 22(21): 5183-5188. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0933.
- Grogan J et al. The immunoreceptor TIGIT regulates anti-tumor immunity. J Immunother Cancer. 2016:4(suppl 1):P209.
- Kurtulus S et al. TIGIT predominantly regulates the immune response via regulatory T cells. J Clin Invest. 2015; 125(11): 4053- 4062. doi:10.1172/JCI81187
- Lozano E et al. The TIGIT/CD226 axis regulates human T cell function. J Immunol. 2012;188(8):3869-3875. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1103627.
- Mahnke K, Enk AH. TIGIT-CD155 Interactions in melanoma: a novel co inhibitory pathway with potential for clinical intervention. J Invest Dermatol. 2016;136(1):9-11. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2015.10.048.
- Pauken KE, Wherry EJ. TIGIT and CD226: tipping the balance between co stimulatory and coinhibitory molecules to augment the cancer immunotherapy toolkit. Cancer Cell. 2014;26(6):785-787. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2014.11.016.
- Stanietsky N et al. The interaction of TIGIT with PVR and PVRL2 inhibits human NK cell cytotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(42): 17858-17863. doi:10.1073/pnas.0903474106
- Yu X al. The surface protein TIGIT suppresses T cell activation by promoting the generation of mature immunoregulatory dendritic cells. Nat Immunol. 2009 Jan;10(1): 48-57. doi: 10.1038/ni.1674. Epub 2008 Nov 16.
- Zhu X et al. Identification of CD112R as a novel checkpoint for human T cells. J Exp Med. 2016;213(2):167-176. doi:10.1084/jem.20150785
-
Bilder

Colon-Carcinoma-20x 
DIA-TG1_WB 
Hashimoto-thyreoiditis-20x_ 
Sarkoidose-20x_ 
T-cell_co-signaling_receptors_and_ligands 
Tonsille-20x
